Types of Bacterial Diseases in Shrimp
Shrimp diseases caused by bacteria can pose a serious threat to farmers. In recent years, these diseases have frequently attacked shrimp farms, becoming a significant risk factor leading to a drastic reduction in shrimp production and economic losses.
The shrimp farming industry plays a crucial role in meeting global seafood demands rich in protein, essential amino acids, and micronutrients. Consequently, producers continually innovate to develop this industry, such as implementing high-density stocking like in super-intensive culture systems.
However, this innovation comes with increased risks of infections and shrimp disease outbreaks. This necessitates constant vigilance for shrimp farmers and the entire vannamei shrimp aquaculture industry.
After discussing viral shrimp diseases previously, this article will delve further into bacterial-induced shrimp diseases.
Also Read: Vannamei Shrimp Probiotics and Its Benefits For Cultivation
Types of Shrimp Diseases Caused by Bacteria
1. Vibriosis
Vibriosis is a shrimp disease caused by Vibrio bacteria and can cause high mortality rates worldwide. Vibrio bacterial infections can occur from the hatchery to the grow-out ponds. Typically, the introduction of Vibrio bacteria into grow-out ponds occurs due to environmental factors, often carried by carrier animals. Shrimp gills are the most vulnerable area due to their thin exoskeleton covering.
Vibrio harveyi is the bacterium most frequently causing mass mortality in a relatively short period. It attacks shrimp larvae at zoea, mysis, and post-larval stages.
Shrimp diseases resulting from Vibrio infections include loose shell syndrome (LSS) and white gut disease (WGD). Both diseases can cause massive mortality during shrimp farming.
2. AHPND
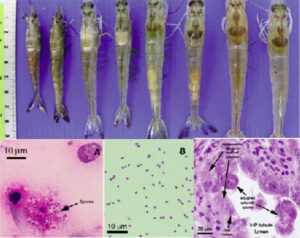
The second bacterial shrimp disease is AHPND (Acute Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Disease) caused by an infection from Vibrio parahaemolyticus bacteria capable of producing toxins leading to shrimp mortality rates of up to 100%.
Deaths due to AHPND occur within 40 days after stocking in ponds. Shrimp affected by this disease exhibit empty digestive tracts, pale and shriveled hepatopancreas, soft skin, and black spots on the hepatopancreas. Typically, deaths occur around the 10th day after stocking, and weakened shrimp sink to the pond bottom before dying.
3. White Feces Disease (WFD)
Another bacterial shrimp disease is White Feces Disease (WFD), resulting from declining water quality and accumulated feed residues in ponds, leading to the formation of organic compounds. It is characterized by long white feces in the ponds. Its effects on shrimp include skin shedding and the presence of worm-like parasites in the intestines, reducing feed efficiency, inhibiting shrimp growth, and significantly decreasing survival rates.
4. Black Spot Disease
Black Spot Disease caused by Vibrio anguillarum can spread in aquatic environments. This disease results in black and brown spots on the shells of affected shrimp. Contributing factors include poor water quality and the accumulation of organic feed residues at the pond bottom. Typically, this disease occurs post-harvest.
Also Read: Get to Know Myo IMNV Disease in Vannamei Shrimp and Its Characteristics
Sources of Bacterial Diseases in Shrimp
1. Environment
The environment can trigger the emergence of bacterial diseases in shrimp. Environmental factors encompass various parameters of pond water quality where shrimp live. The most influential water quality parameters are organic material content and temperature.
Research conducted by the Fisheries Research Institute has proven that organic material significantly affects the increased population rate of Vibrio harveyi bacteria. Rich and high organic content water often originates from waste.
Bacteria are generally fluctuating and can infect and cause shrimp deaths in poor water quality conditions. To mitigate this, practices such as pond draining and efficient feed provision are essential.
Additionally, water temperature significantly affects shrimp metabolism. Normal metabolic processes occur when the water temperature is optimal. Below-optimal temperatures induce stress and worsen shrimp health.
2. Broodstock Contamination
Bacterial diseases in shrimp can horizontally transmit from broodstock to larvae. Infected broodstock releases tissue and ovary fluids together with eggs, allowing pathogens in the fluid to adhere to the eggs. When the eggs hatch into larvae, they become infected with the pathogen. If these larvae are cultivated, their survival rates decrease due to disease susceptibility.
Control and Prevention Measures
1. Effective Environmental Management
To prevent bacterial diseases in shrimp, maintaining good pond environmental management is crucial. This includes ensuring all water quality parameters are at optimal levels.
2. Hygienic Farming Equipment Maintenance
During shrimp farming, avoid using the same farming equipment between ponds. Using the same equipment interchangeably can spread bacterial contamination to other farming ponds.
3. Proper Feed Management
Bacterial accumulation in ponds is often due to poorly processed organic waste from uneaten feed settling at the pond’s bottom. Therefore, controlling shrimp feed provision is crucial.
4. Routine Monitoring
Regular checks are essential in preventing bacterial-induced shrimp diseases. Routine monitoring, usually done through PCR testing at specific stages of the shrimp, helps identify fluctuations in water quality.
Also Read: 5 Things You Need to Do When Starting a Shrimp Farm Business
Perform Routine Shrimp Health Checks with AquaCheck!
Routine shrimp health checks can be a preventative step against bacterial-induced shrimp diseases. Regular PCR tests help prevent widespread shrimp diseases, averting more significant losses.
For those seeking shrimp PCR facilities, consider AquaCheck! AquaCheck is DELOS’s PCR testing service, assisting in detecting up to five pathogens simultaneously at an affordable price.
Moreover, AquaCheck can detect various samples universally, including larvae, shrimp, sediment, water, and other potential pathogen carriers in ponds.
Contact DELOS at contact@delosaqua.com or submit inquiries through our website’s contact column at www.delosaqua.com. Check your shrimp’s health condition with AquaCheck!