Types of Exported Shrimp Products

Shrimp stands as one of Indonesia’s largest export commodities entering the global market. The variety of shrimp products exported is quite diverse, ranging from frozen shrimp, shrimp in head-on form, headless shrimp, and more.
Indonesian shrimp has gained significant traction in the international market due to its relatively high quality compared to other countries. So, what are the types of shrimp products that the global export market demands?
Also Read: Dynamics of Vannamei Shrimp Market and Its Influence on Prices
Types of Exported Shrimp Products
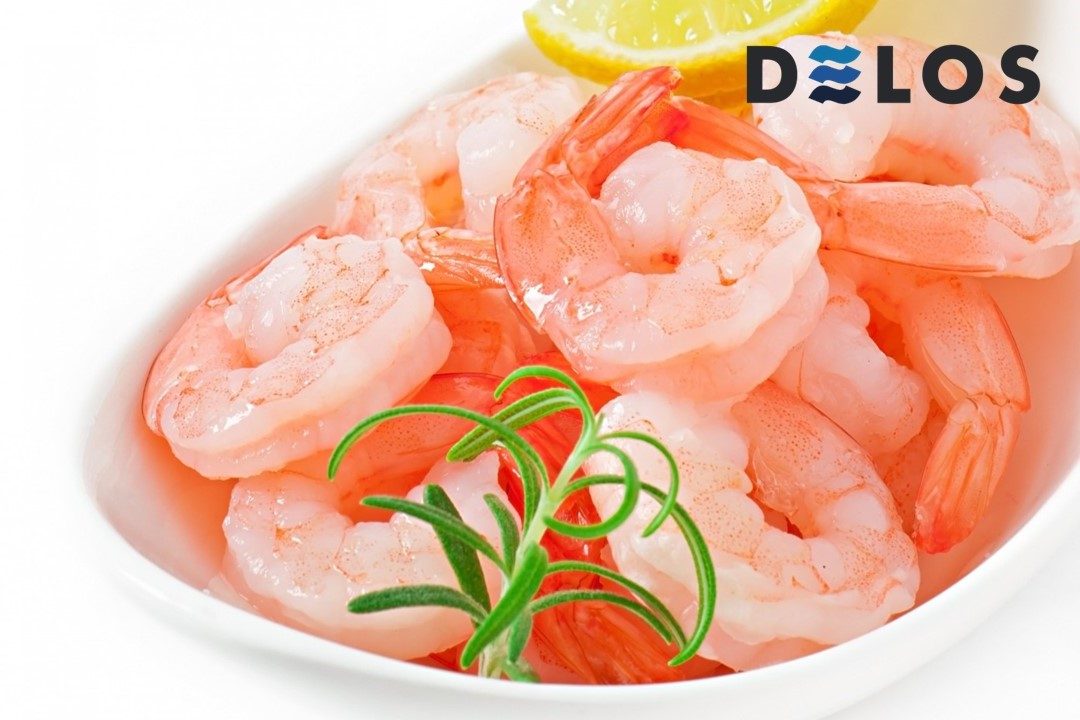
1. Frozen Shrimp
The most sought-after shrimp product in the export market is frozen shrimp. This type of product occupies up to 80% of the total exported shrimp. Typically, frozen shrimp is used as an ingredient in making tempura.
Frozen shrimp products come in various sizes and types, such as vannamei shrimp and tiger prawns, frozen in whole form, head-on, headless, peeled, and nobashi.
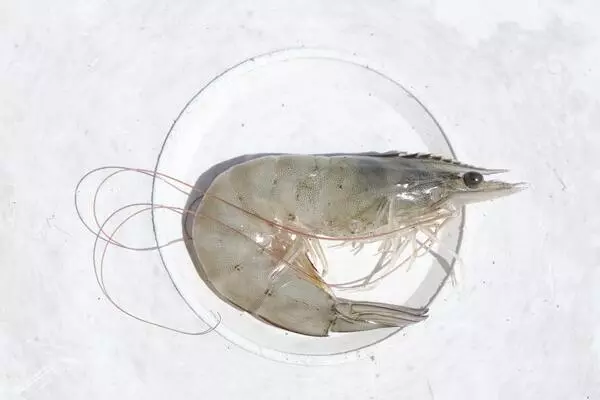
2. Shrimp in Head-On Form
Shrimp products in the head-on form are exported as a whole body without undergoing the process of peeling or head removal.
Head-on shrimp products are highly favoured in Asian markets because the shrimp’s head maintains a distinctive flavour and is considered an added value for consumers who prefer to cook shrimp with the head intact for a stronger taste
Also Read: Want to Get Fair Trade Certification for Shrimp Exports? Here’s The Way!
3. Shrimp in Headless Form
Conversely, shrimp products in headless form do not have a head, making them easier to process and prepare. These products are popular among consumers who prefer the convenience of not having to remove the head before cooking and consuming.
4. Peeled Shrimp
Peeled shrimp refers to shrimp with the outer shell removed, making them ready for consumption without the need to clean the head, shell, or tail first. Peeled shrimp is also subdivided into several types:
a. Peeled Tail On
This type of shrimp product is marketed with the head and shell removed, while the tail remains intact.
b. Peel Deveined Tail On
The Peel Deveined Tail On shrimp is almost similar to Peeled Tail On. However, the distinguishing factor between these two products lies in the cleaning process, which involves carefully deveining the shrimp from the first to the fifth segment.
c. Peeled and Deveined
This shrimp product has been both peeled and deveined, including the tail, making it ready for immediate consumption.
d. Peeled Undeveined
Unlike other shrimp types, Peeled Undeveined shrimp is peeled but still has dirt on its back.
e. Butterfly
Butterfly shrimp is similar to Peel Deveined Tail On shrimp. All parts of the shrimp are cleaned except for the tail and the underside of the abdomen, which is cleaned without cutting it, while the dirt on its underside is removed.
5. Dried Frozen Shrimp
Dried frozen shrimp is also highly sought after in the international market. This type of shrimp is commonly used in making tempura and sushi.
Also Read: HACCP Certification: Procedures, Requirements, and How to Obtain It
Begin Your Shrimp Export Journey with DELOS!
The exported types of shrimp products vary significantly, usually depending on market demand. Each market has its preferred types of shrimp. For instance, the Japanese market favours frozen headless shrimp over other types.
After reading about the various shrimp products exported above, are you starting to consider exporting shrimp abroad? If so, finding the right partner is crucial.
You can choose DELOS AquaLink as your shrimp export partner! With AquaLink, you can export shrimp at the best prices.
Contact the DELOS team at contact@delosaqua.com or submit through the contact form on our website www.delosaqua.com. Start exporting vannamei shrimp with DELOS!