Addressing Harmful Algal Blooms in Shrimp Ponds
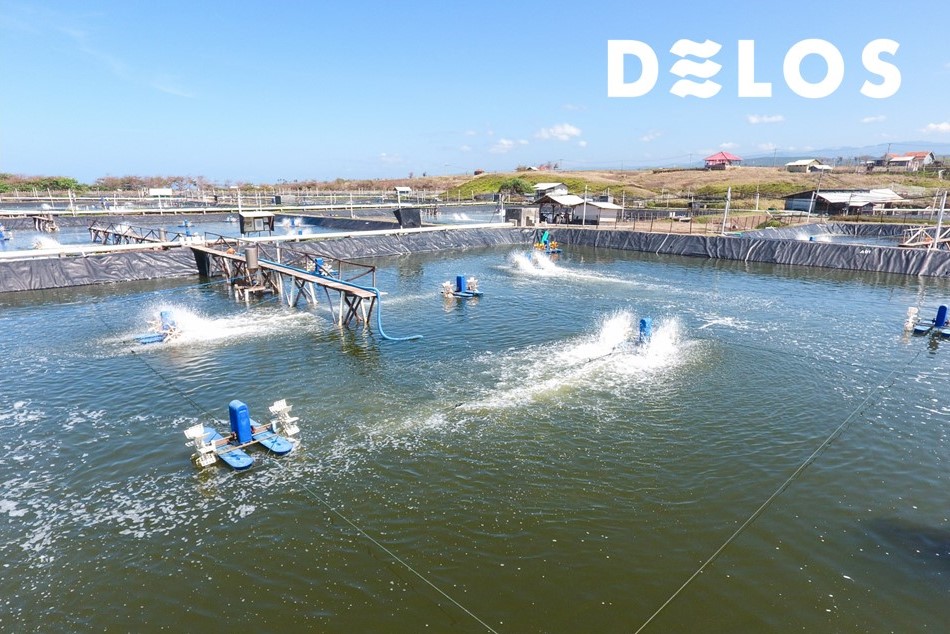
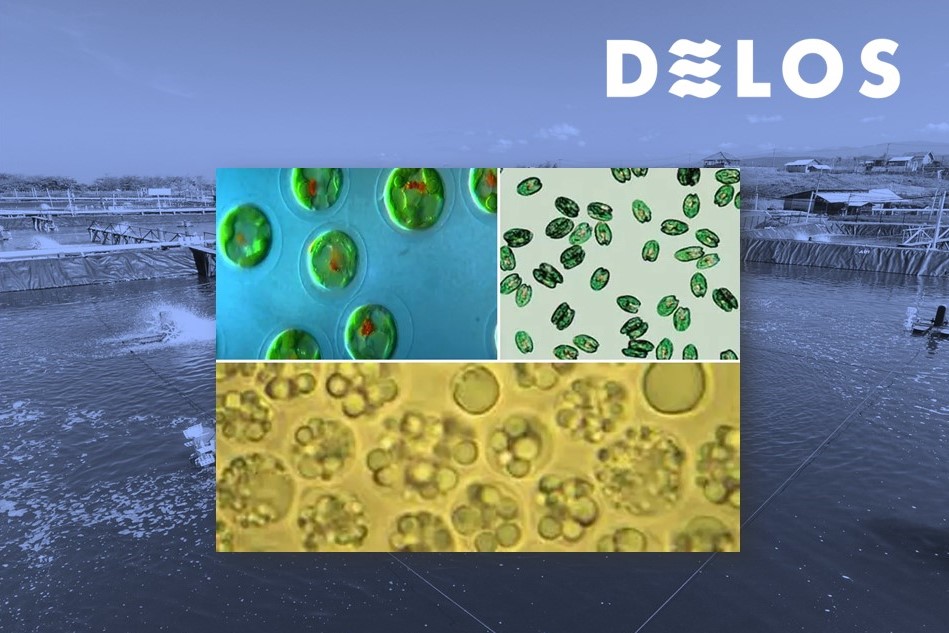
In the cultivation of vannamei shrimp, various types of algae or plankton exist within the shrimp ponds. The presence of diverse plankton indicates that the pond environment is stable and healthy. However, harmful algal blooms, or a sudden increase in the number of plankton, can be detrimental to the shrimp’s survival.
Harmful algal blooms or plankton explosions occur when there is a rapid rise in the population of algae in the pond, causing a change in the colour of the pond water. These blooms can be harmful to shrimp as certain types of algae can release toxins.
What is Algae?

Algae, also known as phytoplankton, are microscopic organisms that move freely and float in the pond water. The presence of algae directly affects the colour of the pond water.
In vannamei shrimp farming, algae serve as both a natural shrimp feed and a source of oxygen beneficial for shrimp respiration. However, the presence of algae must be consistently controlled to avoid harmful algal blooms that can threaten shrimp survival.
Also Read: Treat or Toxin: Plankton – Friend or Foe?
Importance of Algae in Shrimp Ponds
1. Oxygen Source
Algae play a crucial role as suppliers of more than 30% of the total oxygen needed by vannamei shrimp in the pond. This oxygen is produced through photosynthesis during daylight with the assistance of sunlight.
However, in intensive to super-intensive vannamei shrimp farming, additional oxygen supply through the use of aerators is typically required.
2. Natural Shrimp Feed
The presence of algae in the vannamei shrimp farming industry is essential and valuable. These microscopic organisms serve as a food source for shrimp larvae. As a natural feed, the presence of algae in the pond needs to be controlled daily.
3. Pollution Indicator
Algae can also indicate contamination in your shrimp pond, particularly when their growth becomes uncontrolled. This is caused by increased mineral content in the water due to agricultural chemicals and fertilizers rich in nitrogen and phosphorus.
What is Algal Blooming?
Algal blooming refers to a rapid increase in the accumulation of algae populations within shrimp ponds. This occurrence is usually identified by changes in the pigment color of the water.
Algal blooming results from an excessive accumulation of nitrogen or phosphorus fertilizers in the pond environment, leading to excessive algae growth. Algal blooms can be detrimental to vannamei shrimp farming, such as preventing sunlight from entering the ponds and causing a decrease in oxygen levels in the water.
Causes of Algal Blooms
1. Nutrient Excess
Excessive nutrients can lead to uncontrolled growth in phytoplankton populations in shrimp ponds. The increased population of phytoplankton, also known as algal blooms, is indicated by a change in water colour to a dense green. During algal blooms, the pond loses oxygen intake, and the water’s pH becomes unstable and fluctuates.
2. Presence of Organic Waste
Vannamei shrimp ponds generate a considerable amount of organic waste, originating from unconsumed feed, dead shrimp, and shrimp feces. If this waste is not properly managed, it can lead to uncontrolled algae growth.
Also Read: How to Grow Plankton in Shrimp Ponds
Impacts of Algal Blooms in Shrimp Ponds
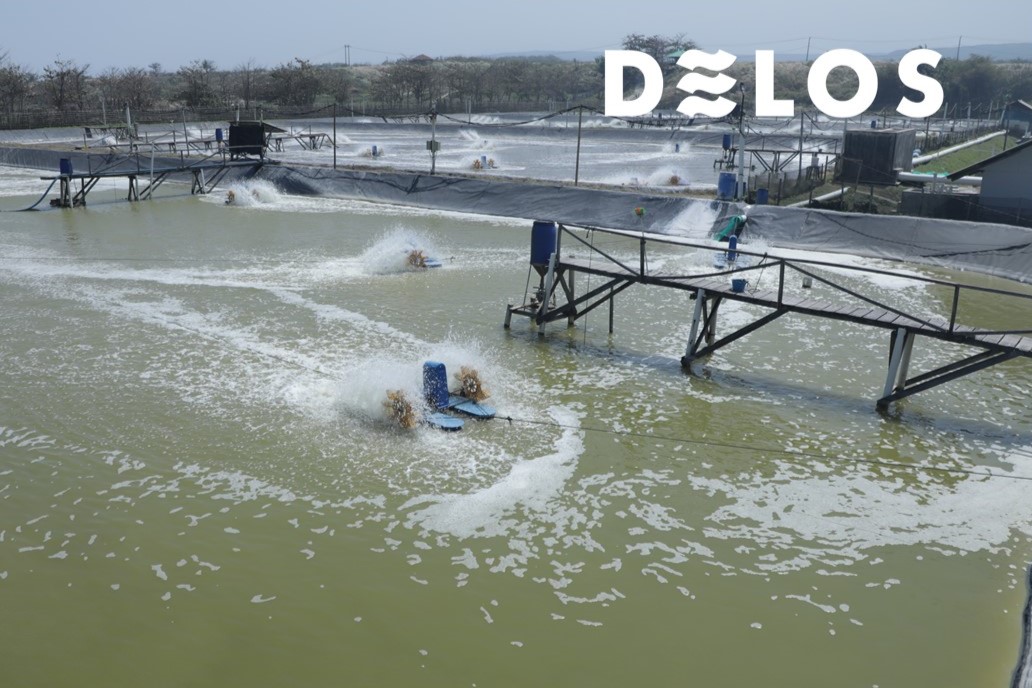
Green-coloured pond water is quite common and indicates a rich plankton environment. However, when plankton populations become excessive, it can have negative effects on shrimp survival.
When plankton populations explode uncontrollably, the pond water becomes densely green. This density prevents sunlight from penetrating the pond, depriving the shrimp of sunlight exposure.
This high density also inhibits proper oxygen circulation. Consequently, shrimp may experience oxygen deficiency, especially if there is no aerator supporting oxygen circulation in the pond.
Ways to Address Algal Blooms in Shrimp Ponds
1. Reducing Pond Nutrient Levels
Reducing nutrients means reducing the amount of feed provided to the shrimp in the pond. This is because excessive, unconsumed feed will settle at the bottom of the pond. This sedimentation can trigger algal blooms.
Therefore, managing proper feed distribution is crucial. This includes reducing the feed provided when the shrimp are in a less voracious feeding phase.
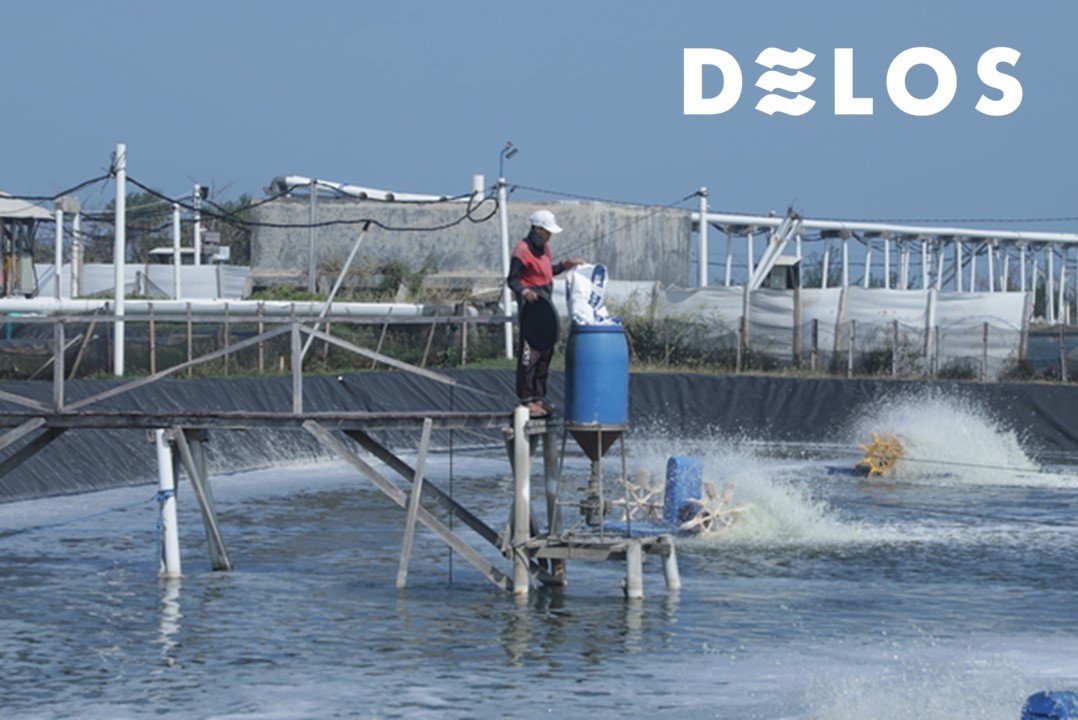
2. Ensuring Proper Aeration
Ponds lacking a proper aeration system can be a triggering factor for the excessive growth of phytoplankton. Thus, ensuring that the existing pond aerators operate continuously is essential for reducing the phytoplankton population.
Poor aeration can lead to the accumulation of waste at the pond bottom. Aeration also helps increase the level of dissolved oxygen in the water.
Also Read: Toxic Substances in Shrimp Ponds: Hidden Threats to Shrimp Survival
Vannamei Shrimp Farming is More Profitable with DELOS!
Algal blooms are a phenomenon that shrimp farmers should be wary of as they can disrupt shrimp survival. Therefore, you must ensure that plankton presence in your pond is well-controlled.
For those who wish to start vannamei shrimp farming, DELOS can be your best aquaculture partner. DELOS is the leading aqua-tech company based on science, technology, and operational management that can help you explore new opportunities in aquaculture.
At DELOS, water quality parameters are checked daily, enabling you to make immediate decisions in case of fluctuations. Moreover, DELOS is supported by the AquaHero application, making it easier for farm owners and personnel to monitor their shrimp ponds daily.
Contact the DELOS team via contact@delosaqua.com or visit our website at www.delosaqua.com to learn more about our services. Start your vannamei shrimp farming journey with DELOS!